From understanding the significance of company culture to practical strategies for implementation, discover how fostering a strong culture drives employee satisfaction, productivity, and success. Explore diverse culture types, assess your current environment, and learn how Leap Onboard can impact organizational culture in this comprehensive guide to company culture.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Company Culture
- The Significance of Company Culture
- How a Strong Culture Impacts Success
- Defining Company Culture
- Emphasis on Shared Values, Behaviors, and Vision
- Types of Company Cultures
- Assessing Your Current Culture
- Steps to Evaluate Your Existing Culture
- Creating Your Ideal Culture
- Defining Your Desired Cultural Attributes
- Aligning Culture with Business Goals and Values
- Implementing Cultural Changes
- Strategies for Fostering a Positive Culture
- The Role of Physical Layout and Artifacts in Shaping Company Culture
- How Leap Onboard Enhances Company Culture
- Real-World Success Stories from Companies with Exceptional Cultures
- Conclusion
Introduction to Company Culture
In the vast landscape of organizational management, few concepts wield as much influence as company culture. It’s the invisible force that shapes how individuals within an organization think, behave, and interact. While often intangible, its impact is undeniable, permeating every aspect of an organization, from its daily operations to its long-term strategic decisions.
The Significance of Company Culture
Company culture is not merely a buzzword; it’s the cornerstone of organizational success. A strong culture breeds employee satisfaction, fuels productivity, and ultimately drives overall success. In today’s hyper-competitive business environment, where talent is the most valuable asset, nurturing a positive culture isn’t just a luxury—it’s a strategic imperative.
How a Strong Culture Impacts Success
Employee satisfaction is intricately linked to company culture. When individuals feel aligned with the values and vision of their organization, they are more engaged, motivated, and fulfilled in their roles. This heightened satisfaction translates into increased productivity, as employees are more likely to invest their time and energy into their work when they feel a sense of purpose and belonging.
Moreover, a strong culture fosters collaboration and innovation, driving the organization forward in an ever-evolving marketplace. Companies with a cohesive culture are better equipped to weather challenges and seize opportunities, positioning themselves for long-term success.
Defining Company Culture
At its core, company culture encompasses the shared values, behaviors, and vision that define an organization. It’s the fabric that binds individuals together and guides their actions. A clear definition of company culture provides the foundation upon which an organization can build and grow.
Emphasis on Shared Values, Behaviors, and Vision
Shared values serve as the moral compass of an organization, guiding decision-making and shaping behavior. Behaviors, on the other hand, are the tangible manifestations of these values, reflecting how individuals interact and collaborate within the organization. Together, they contribute to the overarching vision that unites employees in pursuit of common goals.
Types of Company Cultures
Company cultures come in various forms, each with its own unique characteristics and priorities. From caring workplaces to results-oriented cultures, understanding the different types of cultures can help organizations identify their strengths and areas for improvement.
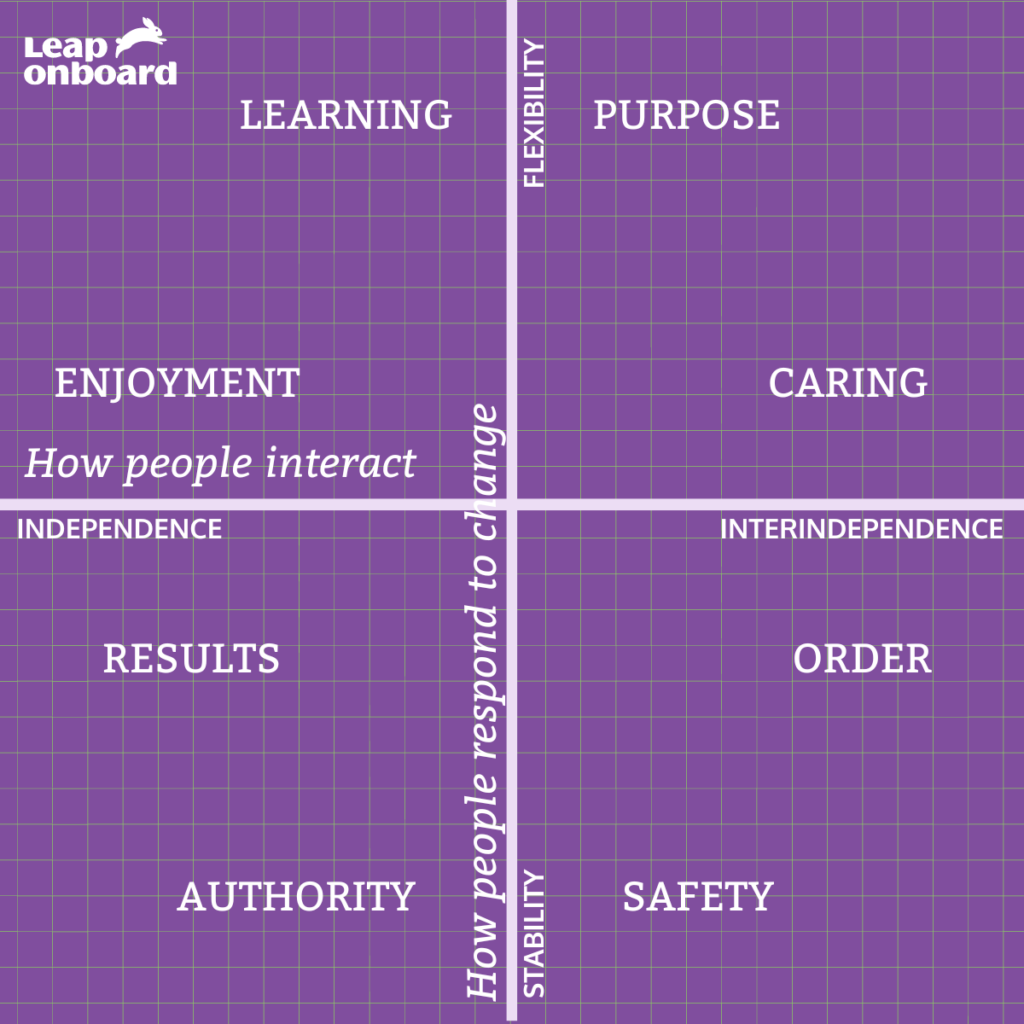
- Caring Workplaces: These cultures prioritize employee well-being and emphasize empathy, support, and inclusivity.
- Purpose-Driven Cultures: Rooted in a strong sense of mission and values, purpose-driven cultures inspire employees to make a meaningful impact beyond financial metrics.
- Learning Cultures: These cultures prioritize continuous learning and development, fostering an environment where curiosity and innovation thrive.
- Playful Work Environments: Characterized by creativity and spontaneity, playful work environments encourage employees to take risks and think outside the box.
- Results-Oriented Cultures: In these cultures, outcomes take precedence over processes, with a focus on achieving measurable results.
- Authority Cultures: Hierarchical in nature, authority cultures emphasize clear lines of authority and decision-making.
- Safe and Risk-Conscious Cultures: These cultures prioritize stability and risk mitigation, valuing caution over bold experimentation.
- Structured and Methodical Work Environments: Characterized by systematic processes and adherence to procedures, structured cultures promote efficiency and consistency.
Each type of culture has its own strengths and weaknesses, and organizations must find the right balance that aligns with their values and objectives.
Assessing Your Current Culture
Before embarking on any cultural transformation journey, it’s essential to assess your organization’s current culture. This process involves gathering employee feedback, conducting surveys, and identifying strengths and weaknesses.
Steps to Evaluate Your Existing Culture
- Conduct employee surveys and focus groups to gather feedback on the current culture.
- Assess cultural artifacts such as office layout, communication channels, and reward systems.
- Analyzing key metrics for recruitment such as employee turnover, engagement levels, and customer satisfaction scores.
- Seek input from leaders and stakeholders to gain a holistic understanding of the organization’s culture.
Creating Your Ideal Culture
Once you have a clear understanding of your current culture, the next step is to define your ideal culture. This involves identifying the cultural attributes that align with your organization’s values and business goals.
Defining Your Desired Cultural Attributes
- Clarify your organization’s mission, vision, and values.
- Identify the cultural traits that support your strategic objectives.
- Articulate your desired culture in concrete terms, focusing on behaviors and attitudes that contribute to success.
Aligning Culture with Business Goals and Values
Culture cannot exist in isolation; it must be aligned with the broader goals and values of the organization. By integrating culture into strategic planning processes, organizations can ensure that cultural initiatives support business objectives.
Implementing Cultural Changes
Cultural transformation is a complex and ongoing process that requires commitment, dedication, and perseverance. Implementing cultural changes involves a combination of strategies aimed at fostering a positive culture and driving behavioral change.
Strategies for Fostering a Positive Culture
- Establish Clear Values: Define core principles that guide decision-making and behavior.
- Foster Employee Engagement: Leverage technology to facilitate communication and collaboration.
- Prioritize Hiring for Culture Fit: Screen candidates based on cultural alignment during the recruitment process.
- Promote Work-Life Balance: Implement policies and programs that support employee well-being.
- Recognize and Reward: Acknowledge and celebrate employee achievements to reinforce desired behaviors.
- Lead by Example: Demonstrate cultural values through actions and behaviors.
- Monitor Metrics: Measure the impact of cultural initiatives on employee satisfaction, productivity, and business outcomes.
- Adapt to Change: Continuously evaluate and adjust cultural initiatives to align with evolving business needs.
The Role of Physical Layout and Artifacts in Shaping Company Culture
Beyond digital platforms and communication channels, the physical layout and artifacts within an organization play a crucial role in setting the tone for company culture. From the layout of office spaces to the design of communal areas, every aspect of the physical environment sends a message about the organization’s values, priorities, and identity. Thoughtfully curated spaces that encourage collaboration, creativity, and social interaction can foster a sense of community and belonging among employees. Likewise, artifacts such as company logos, mission statements, and historical memorabilia serve as tangible reminders of the organization’s heritage and aspirations, reinforcing cultural norms and expectations. By paying attention to the physical environment and leveraging it as a tool for cultural expression, organizations can create spaces that inspire and empower employees to contribute their best selves to the collective mission.
How Leap Onboard Enhances Company Culture
In today’s digital age, effective communication is paramount to cultivating a strong company culture. Leap Onboard, a candidate-to-employee experience platform, offers a seamless solution for HR teams to communicate relevant messages and engage employees from the moment they are interviewed or offered a job by the organization. By leveraging Leap Onboard’s intuitive interface, HR professionals can deliver personalized onboarding experiences tailored to each individual’s role, department, and stage of their journey. From sharing the company’s mission and values to highlighting key policies and initiatives, Leap Onboard empowers HR teams to convey the essence of the organization’s culture in a clear, consistent, and engaging manner to prospective and current employees. Leap Onboard, thereby, enables organizations to foster a sense of belonging and alignment among candidates and employees, driving greater satisfaction, productivity, and retention.
Real-World Success Stories from Companies with Exceptional Cultures
Numerous companies have achieved remarkable success by prioritizing culture and investing in initiatives that foster a positive work environment. From Google’s innovative and collaborative culture to Zappos’ customer-centric and fun-loving culture, these companies serve as inspiring examples of the transformative power of culture.
Conclusion
In today’s rapidly changing business landscape, cultivating a strong company culture isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s a necessity. By defining, aligning, and implementing cultural initiatives, organizations can create environments where employees thrive, innovation flourishes, and success is inevitable. As companies continue to navigate the complexities of the modern workplace, one thing remains clear: culture will always be king.

